5 Effective Ways to Recolor in Adobe Photoshop
Introduction:
Discuss the flexibility of Photoshop as an essential tool for image manipulation, focusing on recoloring techniques.
Emphasize the relevance of recoloring for various professionals in design, photography, and digital art.
Briefly preview the five recoloring methods to be explored.
Section 1: Create a Solid Color Layer as a Clipping Mask
How to create a Solid Color Layer
This is one of my favorite ways to recolor in Adobe Photoshop. Because I use this method so much that I created my own Adobe Photoshop Action for it.
Step-by-Step Guide:
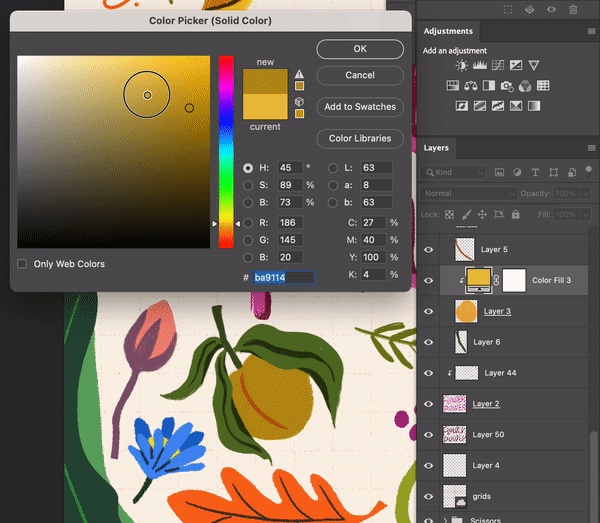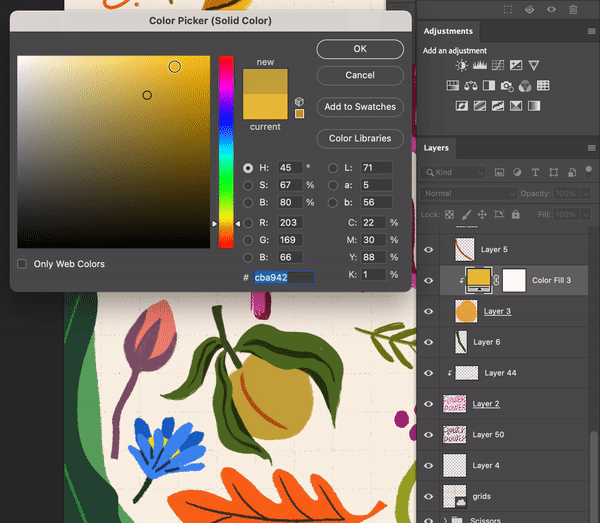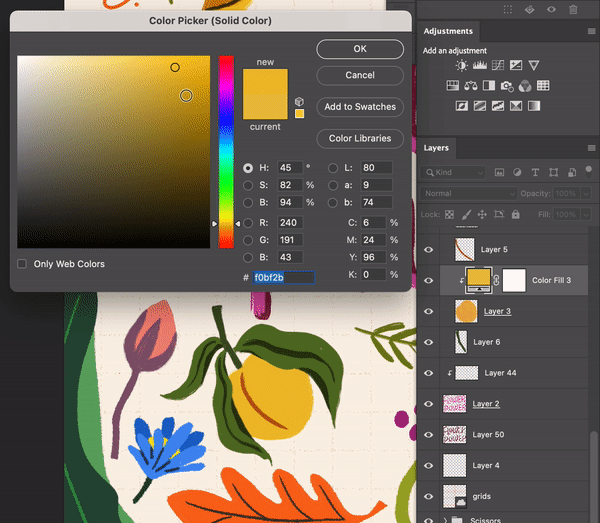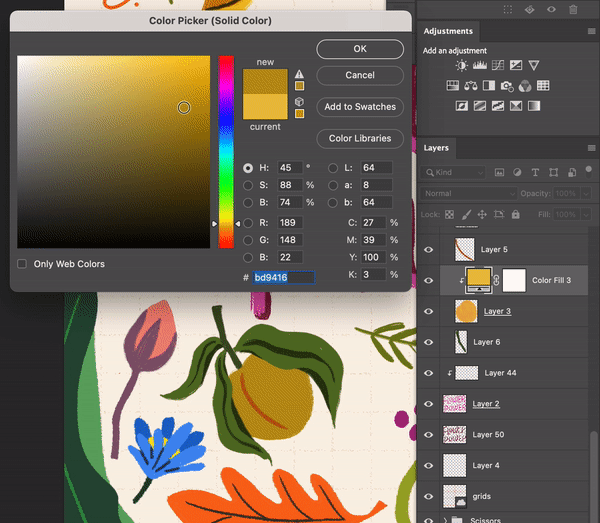
Select Layer > New Fill Layer > Solid ColorChoose a color
Turn the solid color layer into a Clipping Mask
Create a Solid Color Layer as a Clipping Mask
Pros:
Non-Destructive Editing: Solid Color layers allow you to make changes without permanently altering the original image. You can adjust or remove the solid color without any loss of image quality.
Flexibility in Adjustments: You can easily change the color of a Solid Color layer at any time, making it highly flexible for experimenting with different color schemes.
Easy to Apply and Edit: Applying a Solid Color layer is straightforward, and editing it (like changing its blend mode or opacity) is simple, making it accessible even for Photoshop beginners.
Cons:
Limited to a Single Color: Unlike gradient or pattern layers, a Solid Color layer is restricted to one color, which can be limiting if your project requires a more complex color application.
Can Oversimplify Complex Tasks: For detailed color work, like photo retouching or color correction, a Solid Color layer may be too simplistic and might not offer the nuanced control needed.
Requires Understanding of Blend Modes: To fully utilize Solid Color layers, especially for more complex editing tasks, you need a good understanding of blend modes and how they interact with underlying layers.
Section 2: Using the Hue/Saturation Adjustment
The Effect of Hue adjustment Layer
Using the Hue/Saturation Adjustment
Step-by-Step Guide:
Open the image in Photoshop.
Go to 'Layer' > 'New Adjustment Layer' > 'Hue/Saturation'.
In the Hue/Saturation panel, use the hue slider to shift the image’s colors.
Adjust saturation and lightness sliders for finer control.
Practical Applications: Ideal for altering the overall mood or changing specific colors in a photo, like clothing or accessories.
Tips and Tricks: Utilize the 'Colorize' option to apply a single hue across the entire image for a monochromatic effect.
Pros:
Quick and easy to use, ideal for beginners.
Offers a broad range of color adjustments with simple sliders.
Non-destructive editing when used as an adjustment layer.
Cons:
Limited in targeting specific color areas; can affect the entire image if not masked properly.
Less precise control over individual color changes.
Section 3: Selective Color Adjustment Technique
Location of Selective Color in Adobe Photoshop
Detailed Instructions:
Open your image in Photoshop.
Select 'Layer' > 'New Adjustment Layer' > 'Selective Color'.
Choose the color range to adjust from the Colors dropdown menu.
Use the sliders to fine-tune the colors in the selected range.
Best Use Cases: Perfect for refining specific color ranges, such as enhancing greens in landscapes or adjusting skin tones.
Additional Tips: Experiment with adjustments in the neutrals for subtle tonal corrections.
Selective Color in Adobe Photoshop
Pros:
More control over specific color ranges compared to Hue/Saturation.
Able to adjust secondary colors (like yellows in greens).
Useful for fine-tuning colors without affecting the overall balance
Cons:
More complex than basic adjustments, requiring a better understanding of color relationships.
Adjustments can sometimes create unnatural color shifts if not done carefully.
Section 4: The Color Replacement Tool
Location of Replace Color Option in Adobe Photoshop
How to Use:
Select the Color Replacement Tool from the toolbar.
In the options bar, set the brush size and hardness.
Choose the sampling method (Continuous, Once, or Background Swatch).
Adjust tolerance to control the range of colors affected.
Paint over the area you wish to recolor.
Effective Usage: Great for tasks like changing the color of flowers or clothing patterns where precise control is needed.
Expert Advice: Layer masks can be used in conjunction with this tool for non-destructive editing and better precision.
Pros:
Allows for precise recoloring of specific areas without affecting surrounding colors.
Good for quick touch-ups and changes to small elements.
User-friendly with an intuitive brush interface.
Cons:
Not ideal for large-scale or complex color changes.
Can be time-consuming for detailed or intricate areas.
Sometimes struggles with color accuracy in areas with gradients or shadows.
Section 5: Brush Tool for Manual Recoloring
Tutorial on Usage:
Create a new layer and set its blend mode to 'Color'.
Select the Brush Tool and choose a foreground color.
Adjust the brush size, opacity, and flow for the desired effect.
Carefully paint over the areas you want to recolor.
When to Use This Method: Ideal for detailed work like eye color changes or adding color highlights to specific areas.
Professional Tips: Use a tablet for more precise control, and regularly pick colors from the image for a more natural look.
Pros:
Provides the most precise control for detailed recoloring.
Ideal for targeted adjustments like eye color changes or adding highlights.
Flexibility in brush size, opacity, and flow for nuanced editing.
Cons:
Time-consuming, especially for larger areas or complex images.
Requires a steady hand and skill, potentially challenging for beginners.
About Esther Nariyoshi
Hi, I'm Esther, a multidisciplinary illustrator and digital brush creator who loves exploring all mediums, from paper to pixels. I've collaborated with Cloud9 Fabrics and MSU Broad Art Museum, been featured in UPPERCASE Magazine, and share my creative process through Esther's Art Lab, where I teach illustration courses that bridge traditional and digital workflows. My heart finds joy in food and nature illustrations, and I'm passionate about helping artists preserve the authentic energy of hand-drawn work across any medium.
Skip hours of sifting through generalized tutorials, and enjoy a personalized learning session with a laser focus. In a 1-on-1 session, you will receive personalized instruction on how to elevate your digital illustration to the next level based on your own artistic style and preference using Procreate, Adobe Illustrator, and Photoshop, as well as your paper sketchbook.